Star Attention: Efficient LLM Inference Over Long Sequences
Published:
Abstract
Inference with Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) on long sequences is both costly and slow due to the quadratic complexity of the selfattention mechanism. We introduce Star Attention, a two-phase block-sparse approximation that improves computational efficiency by sharding attention across multiple hosts while minimizing communication overhead. In the first phase, the context is processed using blockwise-local attention across hosts, in parallel. In the second phase, query and response tokens attend to all prior cached tokens through sequence-global attention. Star Attention integrates seamlessly with most Transformer-based LLMs trained with global attention, reducing memory requirements and inference time by up to 11x while preserving 95-100% of accuracy.
Introduction
The attention pattern is like this figure:
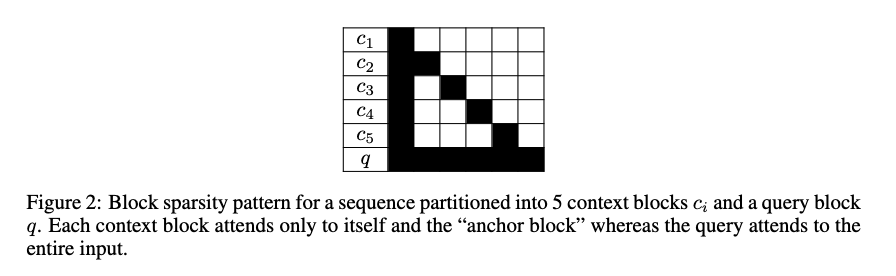
The context blocks have a self-attention and the query block can attend to all tokens before.
The pipeline is consisted of two stages:
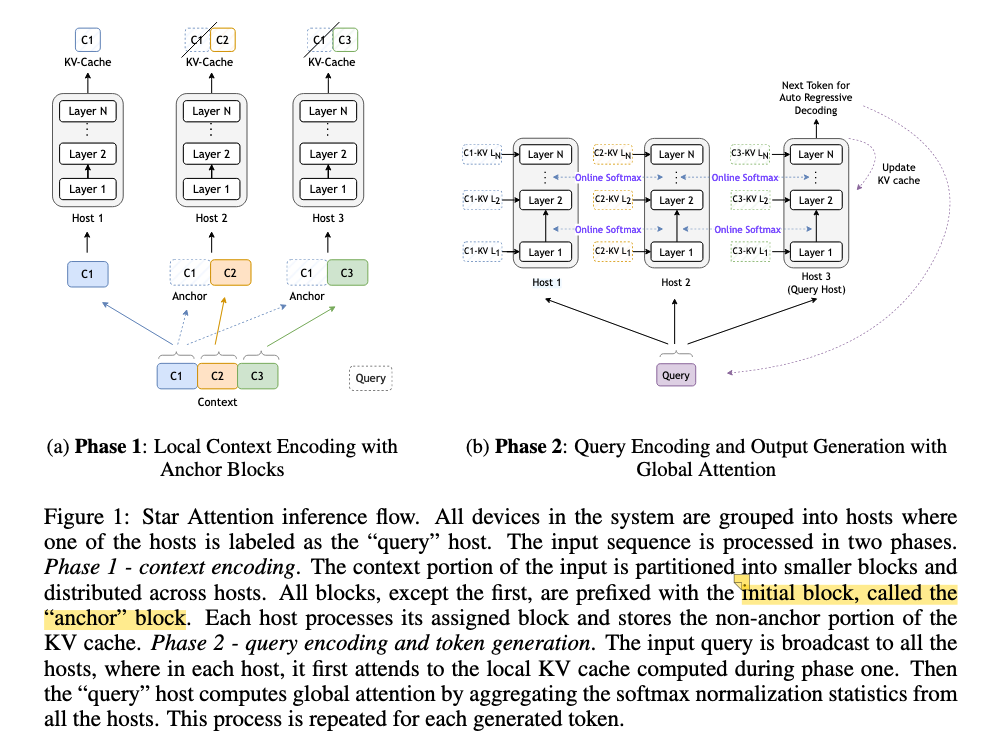
Phase 1: Context Encoding
The context tokens \(c\) are divided into \(\lceil\frac{c}{b}\rceil\) blocks, with each block of the size up to \(b\). Each block is attached with the anchor block in the front. The anchor block plays the role of attention sinks. Then, the augmented blocks were distributed to different hosts, and the local attention was calculated on \(2b\) tokens, and the KV cache is generated.
After that, the KV cache of the anchor block is discarded. (We don’t need KV cache of anchor blocks, the anchor blocks are only used to serve as attention sinks in the prefilling phase and it wouldn’t be used in the decoding phase)
The complexity is linear.
Phase 2: Query Encoding and Token Generation
The query is replicated across all hosts, and the global attention is calculated by two steps:
- Cross attention scores of context block \(c_i\) and query \(q\).
- Online softmax to calculate the global attention weights.
The online softmax needs the communication of a single scalar \(s_h\) (the local sum of exponents) and a vector \(A_h\) (the local attention) per token, which is cheap!
\[A_{\text{global}} = \sum_{h=1}^H \dfrac{s_h}{s_{\text{global}}}A_h\]where
\[s_h = \sum_{k=1}^{l_k} \exp\left(\dfrac{QK_{h,k}^T}{\sqrt{d}}\right)\]Update of Cache and Output
Update the KV cache of the generated token to the contexts on the query host (typically the last host).
Thoughts
- The star structure is taken from the structures of computer networks. (similar to Ring Attention is taken from ring structure)
- The distribution can be successful because the each block of context is independent of each other - so that the calculation of attention can be distributed across hosts without the need of too much communication (only one scaler ad one vector for each host)

Leave a Comment